Mechanism of the Claisen Condensation
Reaction type : Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
Summary
- The Claisen condensation is the ester analogue of the Aldol condensation.
- Reagents : most commonly the base would be the alkoxide, R'O-
- The reaction involves an ester enolate reacting with another molecule of the ester.
- Remember enolates are good nucleophiles and the ester carbonyl C are electrophilic.
- The products of these reactions are b-ketoesters which are important, useful synthetic intermediates.
- Note that the product is the original ester with an acyl group added i.e. an acylation reaction has occurred.
- A simple example of a Claisen condensation is the reaction of ethyl ethanoate which is shown below in two representations:
Step 1:
First, an acid-base reaction. The alkoxide functions as a base and removes the acidic a-hydrogen giving the reactive ester enolate
First, an acid-base reaction. The alkoxide functions as a base and removes the acidic a-hydrogen giving the reactive ester enolate
Step 2:
The nucleophilic ester enolate attacks the carbonyl C of another ester in a nucleophilic substitution process giving the tetrahedral intermediate.
The nucleophilic ester enolate attacks the carbonyl C of another ester in a nucleophilic substitution process giving the tetrahedral intermediate.
Step 3:
The intermediate collapses, reforming the C=O, resulting in loss of the leaving group, the alkoxide, leading to the b-ketoester product.
The intermediate collapses, reforming the C=O, resulting in loss of the leaving group, the alkoxide, leading to the b-ketoester product.
(nguồn: http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/Carey5th/Ch21/ch21-3-1.html
http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/student/olc/graphics/carey04oc/ref/ch21enolatereactions.html)
http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/student/olc/graphics/carey04oc/ref/ch21enolatereactions.html)
More than:
The general form of a Claisen condensation is as follows:
The first step involves adding a strong base to an ester to generate an enolate at the a carbon (note that the enolate has an additional resonance structure).
The enolate can then add to another ester molecule by attacking the carbonyl to make the tetrahedral intermediate. The carbonyl reforms with loss of the alcoxy group to make the b-keto ester.
Example of a Claisen condensation:
This is an example of an intramolecular Claisen reaction, called a Dieckmann condensation.

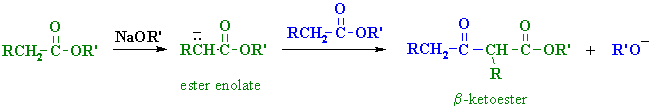




Icon CommentsIcon Comments